Function:
Activated B cells differentiate into either antibody-producing cells called plasma cells that secrete soluble antibody or memory cells that survive in the body for years afterward in order to allow the immune system to remember an antigen and respond faster upon future exposures.At the prenatal and neonatal stages of life, the presence of antibodies is provided by passive immunization from the mother. Early endogenous antibody production varies for different kinds of antibodies, and usually appear within the first years of life. Since antibodies exist freely in the bloodstream, they are said to be part of the humoral immune system. Circulating antibodies are produced by clonal B cells that specifically respond to only one antigen (an example is a virus capsid protein fragment). Antibodies contribute to immunity in three ways: they prevent pathogens from entering or damaging cells by binding to them; they stimulate removal of pathogens by macrophages and other cells by coating the pathogen; and they trigger destruction of pathogens by stimulating other immune responses such as the complement pathway.
The secreted mammalian IgM has five Ig units. Each Ig unit (labeled 1) has two epitope binding Fab regions, so IgM is capable of binding up to 10 epitopes
1) Activation of complement:
Antibodies that bind to surface antigens on, for example, a bacterium attract the first component of the complement cascade with their Fc region and initiate activation of the "classical" complement system.This results in the killing of bacteria in two ways. First, the binding of the antibody and complement molecules marks the microbe for ingestion by phagocytes in a process called opsonization; these phagocytes are attracted by certain complement molecules generated in the complement cascade. Secondly, some complement system components form a membrane attack complex to assist antibodies to kill the bacterium directly.An antibody is a molecule that specificially inactivates an antigen.2) Activation of effector cells:
To combat pathogens that replicate outside cells, antibodies bind to pathogens to link them together, causing them to agglutinate. Since an antibody has at least two paratopes it can bind more than one antigen by binding identical epitopes carried on the surfaces of these antigens. By coating the pathogen, antibodies stimulate effector functions against the pathogen in cells that recognize their Fc region.Those cells which recognize coated pathogens have Fc receptors which, as the name suggests, interacts with the Fc region of IgA, IgG, and IgE antibodies. The engagement of a particular antibody with the Fc receptor on a particular cell triggers an effector function of that cell; phagocytes will phagocytose, mast cells and neutrophils will degranulate, natural killer cells will release cytokines and cytotoxic molecules; that will ultimately result in destruction of the invading microbe. The Fc receptors are isotype-specific, which gives greater flexibility to the immune system, invoking only the appropriate immune mechanisms for distinct pathogens.
3) Natural antibodies:
Humans and higher primates also produce “natural antibodies” which are present in serum before viral infection. Natural antibodies have been defined as antibodies that are produced without any previous infection, vaccination, other foreign antigen exposure or passive immunization. These antibodies can activate the classical complement pathway leading to lysis of enveloped virus particles long before the adaptive immune response is activated. Many natural antibodies are directed against the disaccharide galactose α(1,3)-galactose (α-Gal), which is found as a terminal sugar on glycosylated cell surface proteins, and generated in response to production of this sugar by bacteria contained in the human gut. Rejection of xenotransplantated organs is thought to be, in part, the result of natural antibodies circulating in the serum of the recipient binding to α-Gal antigens expressed on the donor tissue.Immunoglobulin diversity:
Virtually all microbes can trigger an antibody response. Successful recognition and eradication of many different types of microbes requires diversity among antibodies; their amino acid composition varies allowing them to interact with many different antigens. It has been estimated that humans generate about 10 billion different antibodies, each capable of binding a distinct epitope of an antigen. Although a huge repertoire of different antibodies is generated in a single individual, the number of genes available to make these proteins is limited by the size of the human genome. Several complex genetic mechanisms have evolved that allow vertebrate B cells to generate a diverse pool of antibodies from a relatively small number of antibody genes.
- Domain variability:
The complementarity determining regions of the heavy chain are shown in red (PDB 1IGT)
The region (locus) of a chromosome that encodes an antibody is large and contains several distinct genes for each domain of the antibody the locus containing heavy chain genes (IGH) is found on chromosome 14, and the loci containing lambda and kappa light chain genes (IGL and IGK) are found on chromosomes 22 and 2 in humans. One of these domains is called the variable domain, which is present in each heavy and light chain of every antibody, but can differ in different antibodies generated from distinct B cells. Differences, between the variable domains, are located on three loops known as hypervariable regions (HV-1, HV-2 and HV-3) or complementarity determining regions (CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3).
CDRs are supported within the variable domains by conserved framework regions. The heavy chain locus contains about 65 different variable domain genes that all differ in their CDRs. Combining these genes with an array of genes for other domains of the antibody generates a large cavalry of antibodies with a high degree of variability. This combination is called V(D)J recombination discussed below.
- V(D)J recombination:
Simplified overview of V(D)J recombination of immunoglobulin heavy chains
Somatic recombination of immunoglobulins, also known as V(D)J recombination, involves the generation of a unique immunoglobulin variable region. The variable region of each immunoglobulin heavy or light chain is encoded in several pieces—known as gene segments (subgenes). These segments are called variable (V), diversity (D) and joining (J) segments. V, D and J segments are found in Ig heavy chains, but only V and J segments are found in Ig light chains. Multiple copies of the V, D and J gene segments exist, and are tandemly arranged in the genomes of mammals. In the bone marrow, each developing B cell will assemble an immunoglobulin variable region by randomly selecting and combining one V, one D and one J gene segment (or one V and one J segment in the light chain). As there are multiple copies of each type of gene segment, and different combinations of gene segments can be used to generate each immunoglobulin variable region, this process generates a huge number of antibodies, each with different paratopes, and thus different antigen specificities. Interestingly, the rearrangement of several subgenes (e.i. V2 family) for lambda light chain immunoglobulin is coupled with the activation of microRNA miR-650, which further influences biology of B-cells.
After a B cell produces a functional immunoglobulin gene during V(D)J recombination, it cannot express any other variable region (a process known as allelic exclusion) thus each B cell can produce antibodies containing only one kind of variable chain.
- Somatic hypermutation and affinity maturation:
Following activation with antigen, B cells begin to proliferate rapidly. In these rapidly dividing cells, the genes encoding the variable domains of the heavy and light chains undergo a high rate of point mutation, by a process called somatic hypermutation (SHM). SHM results in approximately one nucleotide change per variable gene, per cell division. As a consequence, any daughter B cells will acquire slight amino acid differences in the variable domains of their antibody chains.This serves to increase the diversity of the antibody pool and impacts the antibody’s antigen-binding affinity. Some point mutations will result in the production of antibodies that have a weaker interaction (low affinity) with their antigen than the original antibody, and some mutations will generate antibodies with a stronger interaction (high affinity). B cells that express high affinity antibodies on their surface will receive a strong survival signal during interactions with other cells, whereas those with low affinity antibodies will not, and will die by apoptosis. Thus, B cells expressing antibodies with a higher affinity for the antigen will outcompete those with weaker affinities for function and survival. The process of generating antibodies with increased binding affinities is called affinity maturation. Affinity maturation occurs in mature B cells after V(D)J recombination, and is dependent on help from helper T cells.
- Class switching:
Mechanism of class switch recombination that allows isotype switching in activated B cells
Isotype or class switching is a biological process occurring after activation of the B cell, which allows the cell to produce different classes of antibody (IgA, IgE, or IgG).The different classes of antibody, and thus effector functions, are defined by the constant (C) regions of the immunoglobulin heavy chain. Initially, naïve B cells express only cell-surface IgM and IgD with identical antigen binding regions. Each isotype is adapted for a distinct function, therefore, after activation, an antibody with an IgG, IgA, or IgE effector function might be required to effectively eliminate an antigen.
Class switching allows different daughter cells from the same activated B cell to produce antibodies of different isotypes. Only the constant region of the antibody heavy chain changes during class switching; the variable regions, and therefore antigen specificity, remain unchanged. Thus the progeny of a single B cell can produce antibodies, all specific for the same antigen, but with the ability to produce the effector function appropriate for each antigenic challenge. Class switching is triggered by cytokines; the isotype generated depends on which cytokines are present in the B cell environment.
Class switching occurs in the heavy chain gene locus by a mechanism called class switch recombination (CSR). This mechanism relies on conserved nucleotide motifs, called switch (S) regions, found in DNA upstream of each constant region gene (except in the δ-chain). The DNA strand is broken by the activity of a series of enzymes at two selected S-regions.The variable domain exon is rejoined through a process called non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) to the desired constant region (γ, α or ε). This process results in an immunoglobulin gene that encodes an antibody of a different isotype.
- Affinity designations:
A group of antibodies can be called monovalent (or specific) if they have affinity for the same epitope, or for the same antigen (but potentially different epitopes on the molecule), or for the same strain of microorganism (but potentially different antigens on or in it). In contrast, a group of antibodies can be called polyvalent (or unspecific) if they have affinity for various antigens or microorganisms. Intravenous immunoglobulin, if not otherwise noted, consists of polyvalent IgG. In contrast, monoclonal antibodies are monovalent for the same epitope.Medical applications:
- Disease diagnosis and therapy:
Detection of particular antibodies is a very common form of medical diagnostics, and applications such as serology depend on these methods. For example, in biochemical assays for disease diagnosis, a titer of antibodies directed against Epstein-Barr virus or Lyme disease is estimated from the blood. If those antibodies are not present, either the person is not infected, or the infection occurred a very long time ago, and the B cells generating these specific antibodies have naturally decayed. In clinical immunology, levels of individual classes of immunoglobulins are measured by nephelometry (or turbidimetry) to characterize the antibody profile of patient. Elevations in different classes of immunoglobulins are sometimes useful in determining the cause of liver damage in patients for whom the diagnosis is unclear.
For example, elevated IgA indicates alcoholic cirrhosis, elevated IgM indicates viral hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis, while IgG is elevated in viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis and cirrhosis. Autoimmune disorders can often be traced to antibodies that bind the body's own epitopes; many can be detected through blood tests. Antibodies directed against red blood cell surface antigens in immune mediated hemolytic anemia are detected with the Coombs test. The Coombs test is also used for antibody screening in blood transfusion preparation and also for antibody screening in antenatal women. Practically, several immunodiagnostic methods based on detection of complex antigen-antibody are used to diagnose infectious diseases, for example ELISA, immunofluorescence, Western blot, immunodiffusion, immunoelectrophoresis, and magnetic immunoassay. Antibodies raised against human chorionic gonadotropin are used in over the counter pregnancy tests. Targeted monoclonal antibody therapy is employed to treat diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis,multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, and many forms of cancer including non-Hodgkin's lymphoma,colorectal cancer, head and neck cancer and breast cancer. Some immune deficiencies, such as X-linked agammaglobulinemia and hypogammaglobulinemia, result in partial or complete lack of antibodies.These diseases are often treated by inducing a short term form of immunity called passive immunity. Passive immunity is achieved through the transfer of ready-made antibodies in the form of human or animal serum, pooled immunoglobulin or monoclonal antibodies, into the affected individual.
- Prenatal therapy:
Rhesus factor, also known as Rhesus D (RhD) antigen, is an antigen found on red blood cells; individuals that are Rhesus-positive (Rh+) have this antigen on their red blood cells and individuals that are Rhesus-negative (Rh–) do not. During normal childbirth, delivery trauma or complications during pregnancy, blood from a fetus can enter the mother's system. In the case of an Rh-incompatible mother and child, consequential blood mixing may sensitize an Rh- mother to the Rh antigen on the blood cells of the Rh+ child, putting the remainder of the pregnancy, and any subsequent pregnancies, at risk for hemolytic disease of the newborn.Rho(D) immune globulin antibodies are specific for human Rhesus D (RhD) antigen. Anti-RhD antibodies are administered as part of a prenatal treatment regimen to prevent sensitization that may occur when a Rhesus-negative mother has a Rhesus-positive fetus. Treatment of a mother with Anti-RhD antibodies prior to and immediately after trauma and delivery destroys Rh antigen in the mother's system from the fetus. Importantly, this occurs before the antigen can stimulate maternal B cells to "remember" Rh antigen by generating memory B cells. Therefore, her humoral immune system will not make anti-Rh antibodies, and will not attack the Rhesus antigens of the current or subsequent babies. Rho(D) Immune Globulin treatment prevents sensitization that can lead to Rh disease, but does not prevent or treat the underlying disease itself.
Research applications:
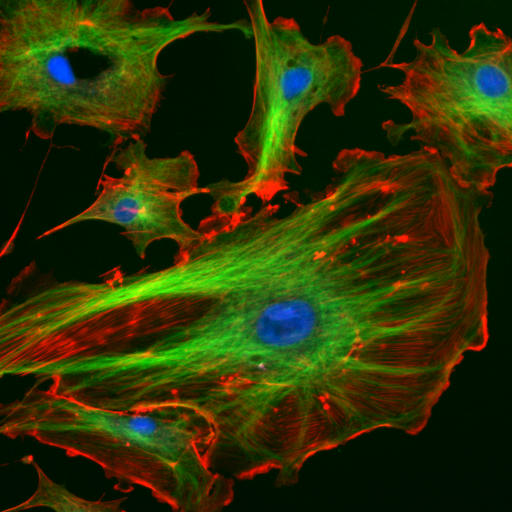
Immunofluorescence image of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Actin filaments are shown in red, microtubules in green, and the nuclei in blue
Specific antibodies are produced by injecting an antigen into a mammal, such as a mouse, rat, rabbit, goat, sheep, or horse for large quantities of antibody. Blood isolated from these animals contains polyclonal antibodies—multiple antibodies that bind to the same antigen—in the serum, which can now be called antiserum. Antigens are also injected into chickens for generation of polyclonal antibodies in egg yolk.
To obtain antibody that is specific for a single epitope of an antigen, antibody-secreting lymphocytes are isolated from the animal and immortalized by fusing them with a cancer cell line. The fused cells are called hybridomas, and will continually grow and secrete antibody in culture. Single hybridoma cells are isolated by dilution cloning to generate cell clones that all produce the same antibody; these antibodies are called monoclonal antibodies. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies are often purified using Protein A/G or antigen-affinity chromatography.
In research, purified antibodies are used in many applications. They are most commonly used to identify and locate intracellular and extracellular proteins. Antibodies are used in flow cytometry to differentiate cell types by the proteins they express; different types of cell express different combinations of cluster of differentiation molecules on their surface, and produce different intracellular and secretable proteins. They are also used in immunoprecipitation to separate proteins and anything bound to them (co-immunoprecipitation) from other molecules in a cell lysate, in Western blot analyses to identify proteins separated by electrophoresis, and in immunohistochemistry or immunofluorescence to examine protein expression in tissue sections or to locate proteins within cells with the assistance of a microscope. Proteins can also be detected and quantified with antibodies, using ELISA and ELISPOT techniques.
REFERENCE:











0 comments:
Post a Comment